One of the greatest benefits to OpenShift hosted control planes (HCP) is that it makes Red Hat OpenShift operational management easier through reduced upgrade complexity and downtime. For example, in a traditional situation you’d be upgrading both the control plane and the workers. With HCP, you’re just upgrading the workers in most cases, thus reducing the risk and turnaround time normally associated with standalone installations. For a visual representation of the difference between a standalone setup and HCP, see Figure 1.

In this article I’m going to run through upgrading a decoupled worker/node cluster (or NodePool in this case) hosted on HCP and point out some of the current caveats and things to look out for.
For this demonstration we’ll be starting out with an OpenShift 4.14.24 bare metal “management cluster” or “hosting cluster” and utilizing the OpenShift Virtualization (KubeVirt) cluster (KubeVirt provider in HyperShift speak) that we provisioned as a “hosted cluster”.
Just for context, I did the provisioning of the “hosted cluster” via the command line like this:
$ hcp create cluster kubevirt \
--name cluster1 \
--release-image quay.io/openshift-release-dev/ocp-release:4.14.24-multi \
--node-pool-replicas 3 \
--pull-secret /path/to/pull-secret.txt \
--memory 8Gi \
--cores 2Let’s begin.
We’ll be utilizing the OpenShift Advanced Cluster Management UI. Our HCP clusters are displayed here and we’ll see that the current version of our KubeVirt cluster is 4.14.24 and there’s an upgrade available. See Figure 2.
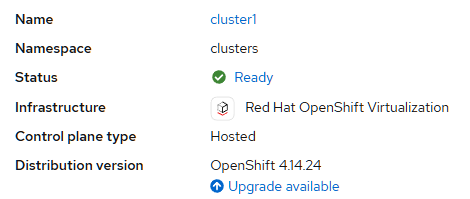
You can also see the new cluster version from the command line by getting the HostedCluster object in the clusters namespace like so:
$ oc get hostedcluster cluster1 -n clustersWhich would result in an output like this:
NAME VERSION KUBECONFIG PROGRESS AVAILABLE PROGRESSING MESSAGE
cluster1 4.14.24 cluster1-admin-kubeconfig Completed True False The hosted control plane is availableIf you want a more in-depth look at the HostedCluster object you can dump it with a YAML output:
oc get hostedcluster cluster1 -n clusters -o yamlNow going back to the web console UI, if we select the Upgrade available link you’ll see an interface similar to the following (Figure 3).

From here we can select the version of OpenShift we’d like to upgrade to from the drop down menu. In our case we’ll be upgrading to the latest version of the 4.14 release which at the time of this writing is 4.14.25.
Before updating the OpenShift hosted cluster to a specific version of OpenShift, always read through the release notes and reference the Multi Cluster Engine (MCE) support matrix.
It’s also possible to view the OpenShift versions that the HyperShift Operator installed and running currently supports. For example:
$ oc describe configmap supported-versions -n hypershiftName: supported-versions
Namespace: hypershift
Labels: hypershift.openshift.io/supported-versions=true
Annotations: <none>
Data
====
supported-versions:
----
{"versions":["4.14","4.13","4.12"]}
BinaryData
====
Events: <none>If you do want to upgrade to a higher OpenShift version than the listed supported versions, then an MCE upgrade would be required.
Alternatively, if you’d prefer to do the upgrade from the command line you can update the cluster spec like so:
$ oc -n NAMESPACE patch HostedCluster HCNAME --patch '{"spec":{"release":{"image": "EXAMPLE"}}}' --type=mergeNote that you will have replace the NAMESPACE, HCNAME, and EXAMPLE with the appropriate values in our case here it will look something like this:
$ oc -n clusters patch HostedCluster cluster1 --patch '{"spec":{"release":{"image": "quay.io/openshift-release-dev/ocp-release:4.14.25-multi"}}}' --type=mergeOnce the update is in progress you will see something like this in the HCP UI (Figure 4).

What’s happening here is that HCP sent the upgrade request to the hosted cluster and that cluster (cluster1) is now reporting back it’s status to this single pane of glass which is the Advanced Cluster Manager (ACM) console. This is one instance but it could be automated to upgrade and monitor at scale in the right hands all from this single interface.
You might also be asking yourself, wait, the hosting cluster is at 4.14.24, so how is it possible to run a newer 4.14.25 hosted cluster? It is possible and does work. That is because the “hosting” cluster is completely independent of the “hosted” cluster. That’s a one of the beautiful things about of hosted control planes: the ability to isolate clusters yet maintain them conveniently and effectively.
When the upgrade is complete you’ll see that your screen is updated and simply presented like so (Figure 5).

And if you dive into the console of cluster1 itself you’ll see the following (Figure 6).
Simple as that. A no hassle update of an OpenShift cluster in minutes all from a centralized location.
Thank you HyperShift Operator!
Helpful resources
Knowing the HyperShift API may be of some use. I would highly recommend looking through it and understanding what API resources are available from a HyperShift perspective.
