Red Hat OpenShift GitOps provides Argo CD and other tooling used to implement GitOps workflows for cluster configuration and application delivery. OpenShift GitOps is a Red Hat OpenShift add-on, available as an operator in the OperatorHub. Once you've installed the OpenShift GitOps operator, you can deploy Argo CD instances using Kubernetes custom resources.
OpenShift GitOps deployment modes
OpenShift GitOps supports flexible Argo CD configurations to satisfy diverse user needs in the world of GitOps, as shown in Figure 1.

Cluster-scoped Argo CD
OpenShift GitOps provides single-click enablement of GitOps for OpenShift cluster configuration. When the OpenShift GitOps operator is installed, an Argo CD instance is set up for users out of the box. It comes with the configuration required to configure a cluster in the openshift-gitops namespace, which acts as the GitOps control plane for cluster configuration. Typical cluster configuration activities include configuring control plane operators, setting up developer namespaces, installing Operator Lifecycle Manager (OLM) operators, and managing storage.
Application-scoped Argo CD
You can create additional Argo CD instances to satisfy the needs of software development organizations sharing the same cluster. In this article, we’ll discuss how developers can create independent Argo CD instances for one or more application delivery teams using OpenShift GitOps 1.2.
Application delivery with OpenShift GitOps
To achieve absolute isolation and multitenancy, OpenShift GitOps 1.2 supports the installation of namespace-scoped Argo CD instances for one or more application delivery teams in an organization, as shown in Figure 2.

Setting up a control plane
A GitOps control plane is a namespace where Argo CD is installed. You can express an intent to deploy and sync Kubernetes manifests from Git by creating one or more application custom resources in the GitOps control plane.
To initialize a namespace-scoped Argo CD instance, you can create an Argo CD custom resource (CR) in a new namespace designated to be a GitOps control plane, as shown in the following example. This creates a minimalistic Argo CD instance with privileges to manage the contents of the namespace:
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: ArgoCD
metadata:
name: argocd #name of the Argo CD instance
namespace: foo #namespace where you want to deploy argocd instance
spec:
server:
route:
enabled: true #creates an openshift route to access Argo CD UI
Deploying an application from Git
The following code example shows how you would deploy an application from Git (also see Figure 3):
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: sample-app #app CR name
namespace: foo #argocd instance namespace
spec:
destination:
namespace: foo #namespace where app is deployed
server: 'https://kubernetes.default.svc'
source:
path: app
repoURL: 'https://github.com/redhat-developer/openshift-gitops-getting-started'
targetRevision: HEAD
project: default

Adding projects to the control plane
Create a namespace, bar, and try deploying an application in this namespace, which is managed by the Argo CD instance deployed in the namespace foo.
First, create the namespace bar as follows:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: bar
spec:
finalizers:
- kubernetes
Then, create an application custom resource in the namespace foo:
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: sample-app-2
namespace: foo #namespace where Argo CD instance is installed
spec:
destination:
namespace: bar #target namespace where app is deployed
server: 'https://kubernetes.default.svc'
source:
path: app
repoURL: 'https://github.com/redhat-developer/openshift-gitops-getting-started'
targetRevision: HEAD
project: default
Authorizing the GitOps control plane
The GitOps control plane will try to deploy the application in the namespace bar. As you can see in Figure 4, the sync fails because the GitOps control plane is not authorized to deploy managed resources in the namespace bar.
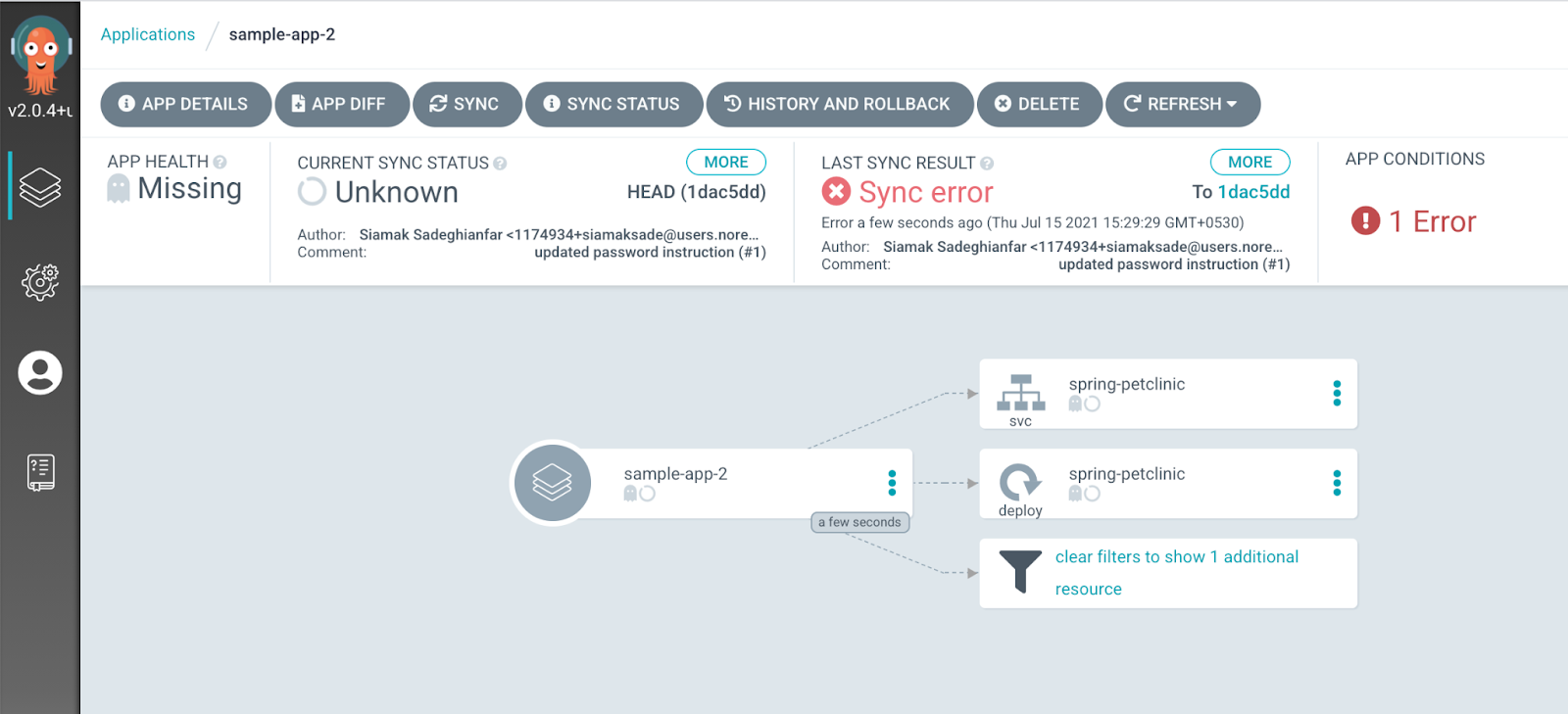
To authorize the GitOps control plane to deploy managed workloads in a namespace, the namespace owner needs to decorate the namespace resource with a label containing the reference to the namespace where the GitOps control plane resides.
The OpenShift GitOps operator reads this expression of intent to have the namespace managed by a specific GitOps control plane and configures the appropriate Argo CD secrets and Kubernetes role-based access control (RBAC).
Label the namespace as follows:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
labels:
argocd.argoproj.io/managed-by: foo #argocd instance ns
name: bar
spec:
finalizers:
- kubernetes
This configures the existing namespace bar with the label recognized by the OpenShift GitOps operator.
After configuring the namespace, trigger the sync from the Argo CD UI. The application will sync successfully, as shown in Figure 5.

bar.Figure 6 shows the developer perspective after the user workload in the namespace bar has been successfully deployed.
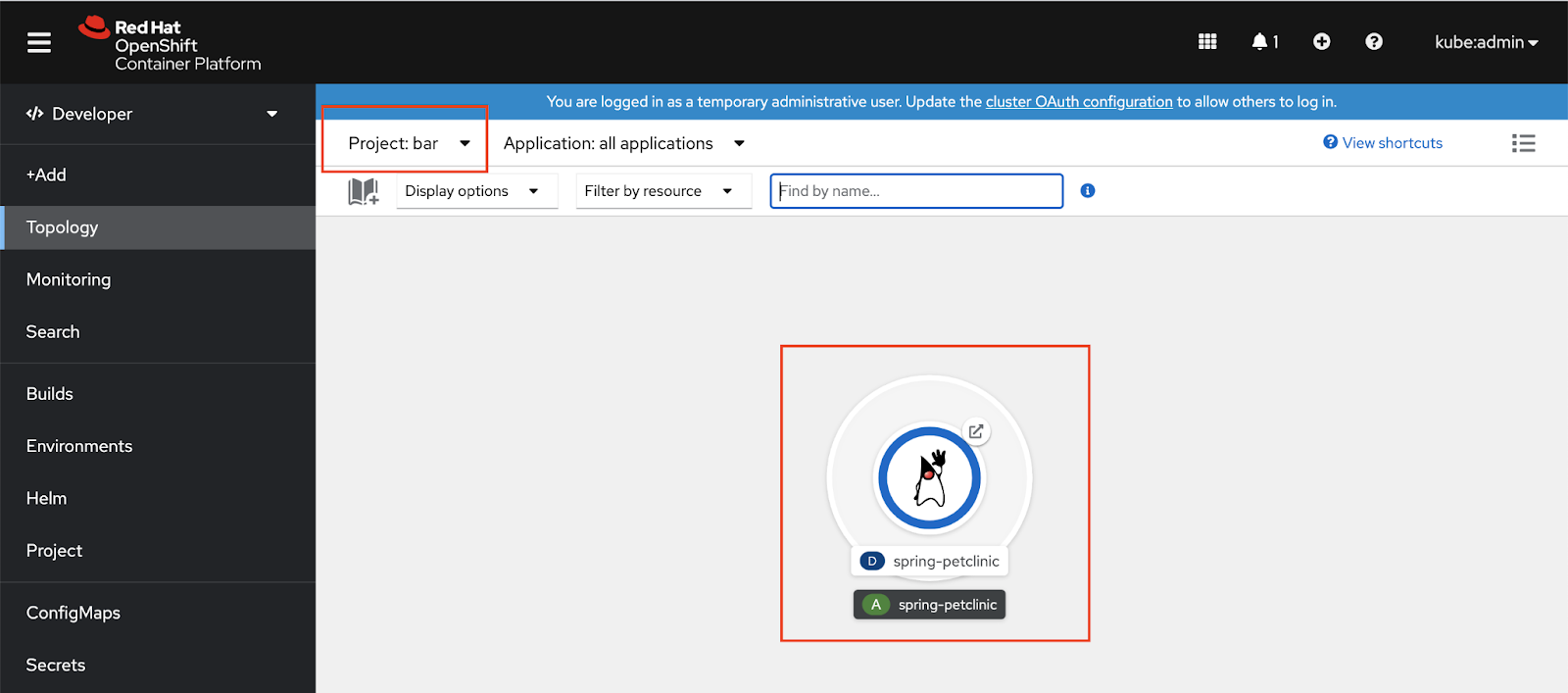
bar.Argo CD configuration in Red Hat OpenShift GitOps
In OpenShift GitOps 1.1.1, a security issue was reported with Argo CD instances configured for application delivery. Handling the vulnerability required significantly curtailing the privileges of Argo CD instances in OpenShift GitOps 1.1.2. This led to upgrading issues and potentially arduous manual configuration of Argo CD instances installed in developer namespaces. These issues showed up in two scenarios:
- When configuring the Argo CD cluster secret.
- When creating a rolebinding in participating namespaces with the Argo CD application controller service account.
While the change was necessary, it became a hurdle to the frictionless operation of Argo CD instances and potentially violated the principles of declarative configuration, while also exposing users to Argo CD's underlying deployment details.
As an enhancement, we fast-tracked the development of a new feature that allows users to authorize the management of OpenShift projects seamlessly:
- A team lead sets up a GitOps control plane for the team in the namespace
my-team. - Members of the team label their own namespaces referring to the
my-teamnamespace indicating that they authorize the GitOps control plane inmy-teamto manage their namespaces.
Conclusion
OpenShift GitOps strives to make it easy for developer teams to manage, configure, and use Argo CD securely for application delivery on OpenShift. As this article demonstrates, application delivery teams can create multiple isolated Argo CD instances on a Red Hat OpenShift cluster. This provides users and administrators with full control over what an Argo CD instance is empowered to do. Optionally, the cluster administrator can use the Argo CD instance in the openshift-gitops namespace to declaratively manage Argo CD instances across multiple developer namespaces.
